Aluminum 3D printing isn’t just a futuristic trend; it’s the secret sauce that’s revolutionizing manufacturing. Imagine crafting lightweight yet robust components with the precision of a laser-guided chef slicing through butter. This technology is making waves across industries, from aerospace to automotive, proving that metal can be as flexible as your favorite yoga instructor.
Table of Contents
ToggleOverview of Aluminum 3D Printing
Aluminum 3D printing utilizes advanced additive manufacturing techniques to produce components with remarkable properties. This process creates lightweight structures that exhibit high strength-to-weight ratios, making them ideal for demanding applications. Additive manufacturing allows for intricate designs that traditional methods can’t easily achieve.
The technology frequently employs aluminum alloys, such as 6061 and 7075, known for their excellent mechanical properties. These materials facilitate improved performance in end-use parts across various sectors. Notably, aerospace and automotive industries leverage aluminum 3D printing to reduce weight while maintaining structural integrity in parts like brackets and housings.
In terms of production efficiency, aluminum 3D printing significantly shortens lead times. Rapid prototyping emerges as a key advantage, enabling quicker iteration cycles during design phases. Furthermore, this method minimizes material waste, contributing to a more sustainable manufacturing practice.
Thermal properties of aluminum also play a crucial role during the printing process. With high thermal conductivity, aluminum components cool quickly, enhancing dimensional accuracy and reducing warping. Various 3D printing technologies, such as powder bed fusion and directed energy deposition, specialize in processing aluminum effectively, providing diverse options for manufacturers.
As industries continue to adopt this technology, ongoing research into alloy development and printing techniques promises to expand its capabilities. Enhanced functionalities may include improved corrosion resistance and thermal stability, further broadening the appeal of aluminum 3D printing.
Benefits of Aluminum 3D Printing
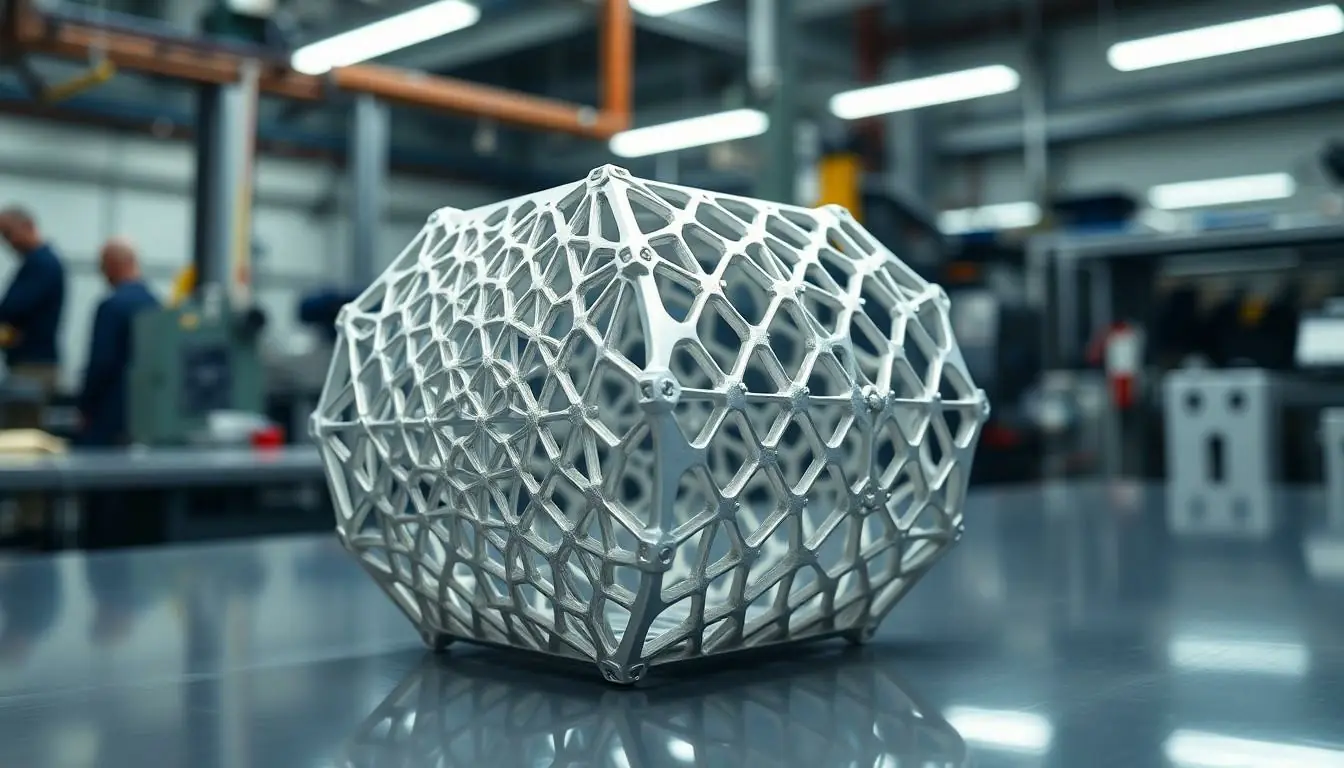
Aluminum 3D printing offers numerous advantages that make it a game-changer in manufacturing. These benefits cater to diverse industrial needs.
Lightweight and Strong
Aluminum components exhibit impressive strength while maintaining a low weight. This combination supports better performance in applications like aerospace, where reducing overall mass is critical. Strength percentages often reach up to 85% of wrought aluminum in printed parts. Engineers leverage this capability to increase fuel efficiency and enhance structural integrity without adding excessive weight. Tailoring the design to minimize material usage further strengthens the overall component economy while supporting complex geometries.
Design Flexibility
Designers benefit significantly from the flexibility aluminum 3D printing affords them. They can create intricate structures and geometries that traditional manufacturing methods cannot achieve. Incorporating lattice structures or embedded features becomes easier with additive manufacturing technologies. Rapid iteration and customization reduce time and costs during the prototyping phase. Industries relying on specialized components, such as automotive and healthcare, find this adaptability vital for innovation. It enables teams to experiment with forms that enhance performance and functionality, pushing the boundaries of what is possible in product design.
Applications of Aluminum 3D Printing
Aluminum 3D printing serves a variety of sectors, delivering lightweight and durable components tailored for specific needs.
Aerospace Industry
In aerospace, aluminum 3D printing plays a critical role in creating complex parts that enhance performance. Components like brackets, housings, and structural elements benefit from the technology’s precision and strength. Utilizing materials such as aluminum alloys allows for reduced weight, which significantly contributes to fuel efficiency. Parts produced using this technique achieve strength levels comparable to traditional forged aluminum, promoting safer and more efficient aircraft. Furthermore, rapid prototyping enables engineers to test and iterate designs swiftly, adapting to changes in specifications without long lead times.
Automotive Industry
In the automotive sector, aluminum 3D printing facilitates innovative designs and customization for various vehicle components. Manufacturers produce lightweight parts like engine mounts, brackets, and even structural components, improving overall vehicle performance. The strength-to-weight ratio maintains structural integrity while minimizing mass, which directly influences fuel efficiency. Flexibility in design permits the creation of intricate geometries, enhancing aerodynamics and aesthetics. As a result, car makers can respond quickly to market trends and consumer demands, allowing for cost-effective production runs without compromising quality.
Medical Sector
The medical sector benefits from aluminum 3D printing by producing customized implants and surgical instruments. This technique allows for the development of lightweight devices that retain strength and biocompatibility. Customization plays an essential role in fitting individual patient needs, leading to improved surgical outcomes. Additionally, the ability to create complex geometries enables better integration with biological systems. By streamlining the production of specialized medical devices, practitioners can enhance patient care. The fast turnaround time also reduces waiting periods for critical components, ensuring timely interventions.
Challenges in Aluminum 3D Printing
Aluminum 3D printing presents several challenges that practitioners must navigate. Understanding these difficulties is crucial for effective implementation.
Material Properties
Material properties introduce significant challenges in aluminum 3D printing. Aluminum’s thermal conductivity affects cooling rates, potentially leading to warping during the process. Inconsistent melting behaviors of different alloys can also impact part reliability. For example, the structural integrity of components may differ based on the selected alloy. Furthermore, defects like porosity can arise, compromising the mechanical strength of the printed parts. Successful aluminum 3D printing requires careful selection and optimization of alloys to mitigate these risks.
Cost Considerations
Cost considerations pose another barrier in aluminum 3D printing adoption. The initial setup for metal 3D printers tends to require substantial investment. High-quality materials such as aluminum powder often come at a premium price, contributing to increased production costs. Operating costs, including maintenance and energy consumption, can significantly affect profitability. Despite these challenges, businesses recognize the long-term savings associated with rapid prototyping and reduced material waste. Evaluating the overall cost-effectiveness remains essential for companies considering this technology.
Future Trends in Aluminum 3D Printing
Aluminum 3D printing continues to evolve, driven by technological advancements and industry demands. Emerging techniques, including improved powder bed fusion methods, enhance efficiency and reduce production times. Researchers focus on developing new aluminum alloys that offer better mechanical properties and corrosion resistance, expanding application potential.
Materials customization plays a crucial role in future innovations. Tailored alloys can optimize strength, weight, and thermal properties, which cater to specific industry needs. Adoption of artificial intelligence and machine learning for process optimization is expected, enabling faster and smarter printing adjustments to improve product quality.
Sustainability is becoming a key focus in aluminum 3D printing. Efforts to minimize material waste through more precise printing processes align with industry trends toward environmentally friendly practices. Companies are investing in methods to recycle aluminum powder, promoting a circular economy within manufacturing.
Collaboration among industries aids in overcoming current challenges. Shared knowledge between sectors can lead to breakthroughs in addressing defects like porosity and warping. Partnerships with research institutions enhance the focus on developing standardized practices, fostering confidence in material performance.
Automation and robotics also influence future trends. Integration of these technologies boosts production capabilities and can lead to lower costs. Such advancements allow manufacturers to respond rapidly to changing market demands, improving overall competitive advantage.
End use cases are likely to expand significantly. With aerospace and automotive applications leading the charge, healthcare and consumer products will increasingly leverage aluminum 3D printing. As designs require greater personalization and functionality, this technology will adapt to meet those needs effectively.
Aluminum 3D printing is reshaping the landscape of manufacturing by delivering lightweight and robust components tailored to industry demands. Its versatility allows for innovative designs that traditional methods can’t achieve, paving the way for advancements in sectors like aerospace, automotive, and healthcare.
As technology progresses, ongoing research into new alloys and printing techniques will enhance the capabilities of aluminum 3D printing. Challenges remain, but the potential for reduced lead times and increased customization positions this technology as a cornerstone of modern manufacturing.
With a focus on sustainability and efficiency, aluminum 3D printing is set to play a critical role in developing the next generation of products that meet both performance and environmental standards. The future is bright for this transformative technology, promising continued growth and innovation.



